In 2012, BLM began a pilot project to implement its National Assessment, Inventory and Monitoring (AIM) Strategy in the National Petroleum Reserve-Alaska (NPR-A). The AIM Strategy focuses on management questions important to land managers at varying levels of the Bureau: from field office to national levels, including status, trend, amount, location, and spatial pattern of important natural resources. Wide ranging management questions across multiple land management programs and scales require coordinated and integrated long-term data collection. AIM is being established in the NPR-A to: 1) quantitatively describe the pre-development ecological status and trend baseline, and 2) ascertain the effectiveness of future adaptive management strategies. AIM will complement existing NPR-A monitoring processes, collect quantitative monitoring data that can be used for many purposes, and provide land managers with the information to develop improved and defensible strategies for the protection and proper development of natural resources across a broad landscape.
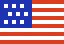
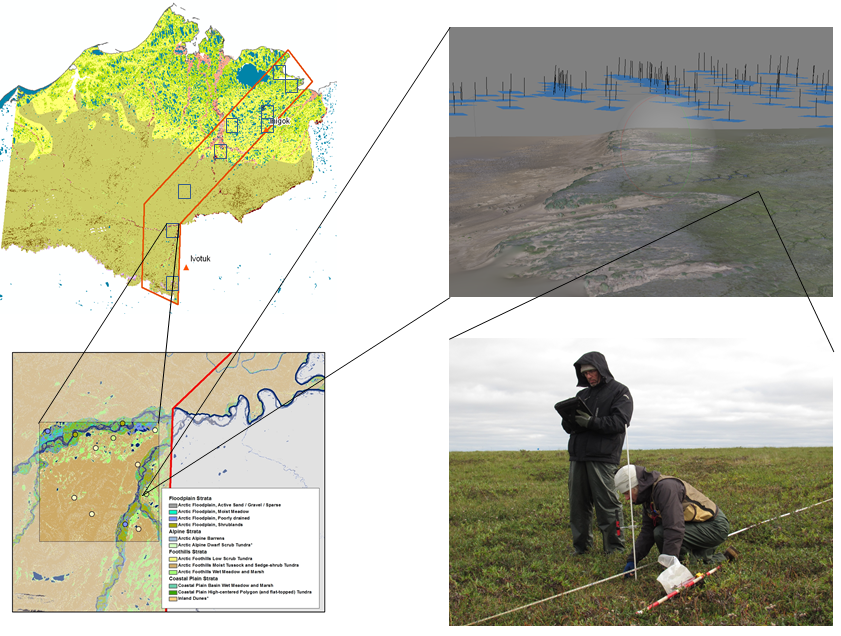
Between July 31 and Aug 7, 2012, field plots along a 30-mile wide N-S transect in the eastern NPR-A were established and visited by helicopter-based field crews collecting field samples and high resolution aerial photos . The goals of this pilot project are to: 1) evaluate AIM core and supplemental indicators and collection methods in tundra ecosystems, 2) evaluate photogrammetry methods for core indicator plot-level data collection, 3) determine effectiveness and efficiencies gained from aerial visits versus on-the-ground sampling, 4) determine variance within each sampling strata, and 5) estimate future costs for broad-scale deployment across the entire NPR-A. Analysis is ongoing with results being published next year.
AIM sampling design, remote sensing, and field data collection in the NPR-A. The figure above highlights the overall structure for the sampling and data collection conducted in August 2012. Ten 10x10 mile frames were randomly selected within the study area (outlined in red). Using vegetation maps of the North Slope, sample plots were selected using a stratified random design. At each field plot, ground crews collected the AIM core indicators using a Line-Point Intercept method while an aerial crew collected 1cm stereo imagery using a Nikon D800 mounted on a helicopter. The ground and aerial imagery will be analyzed to identify which AIM core indicators can accurately be estimated remotely.