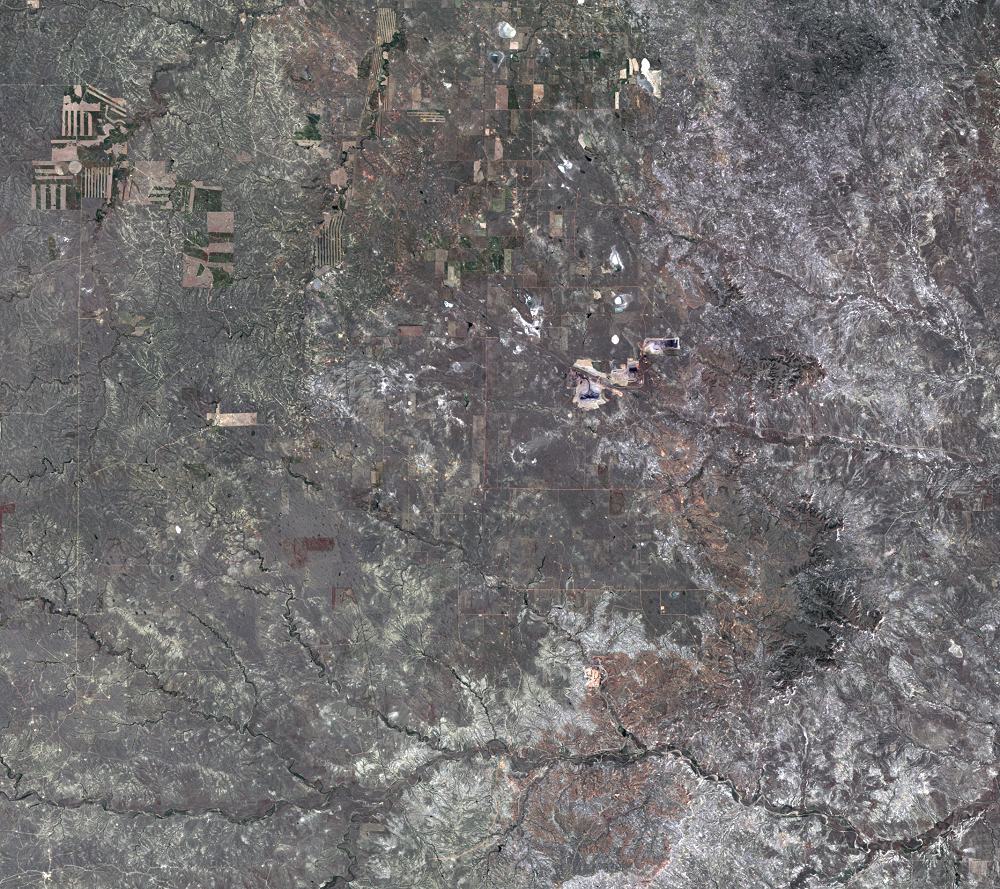
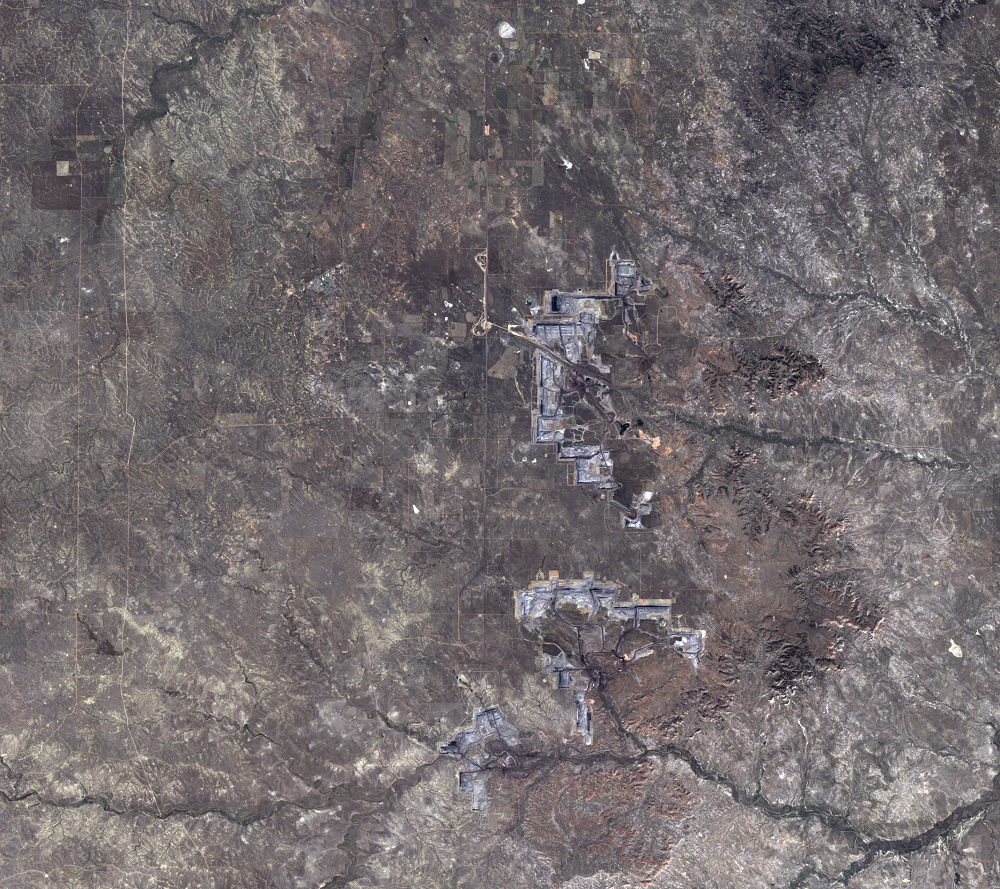
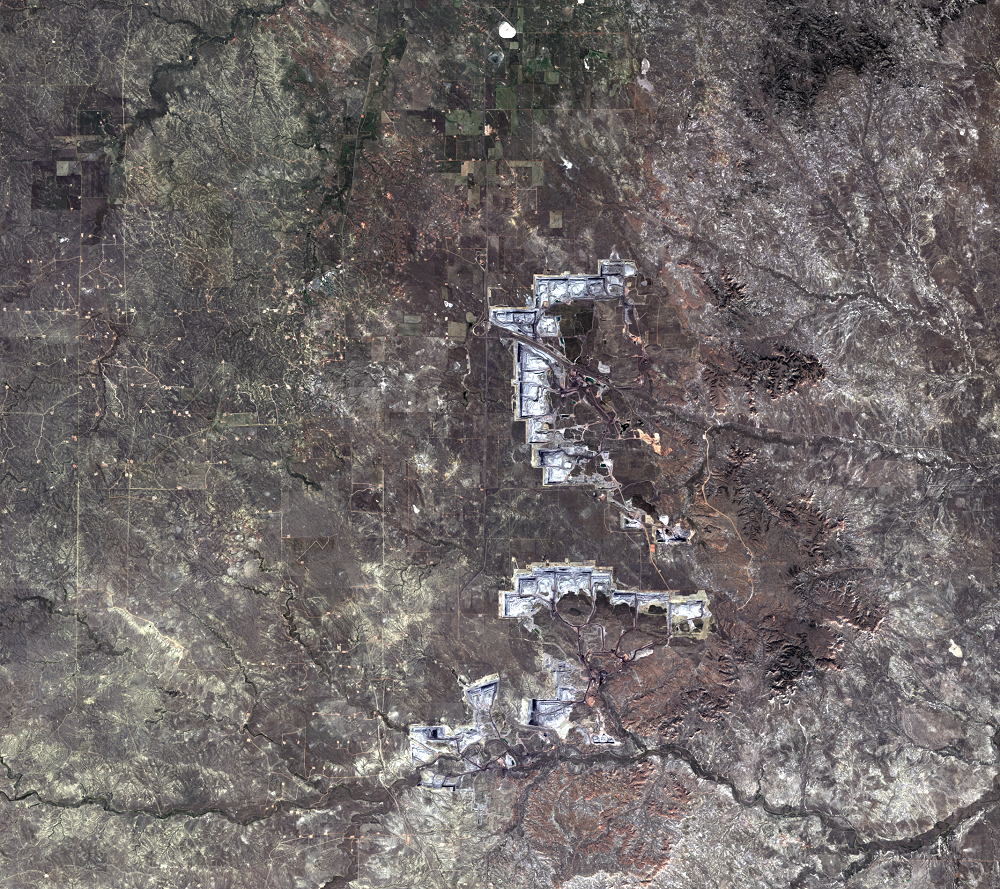
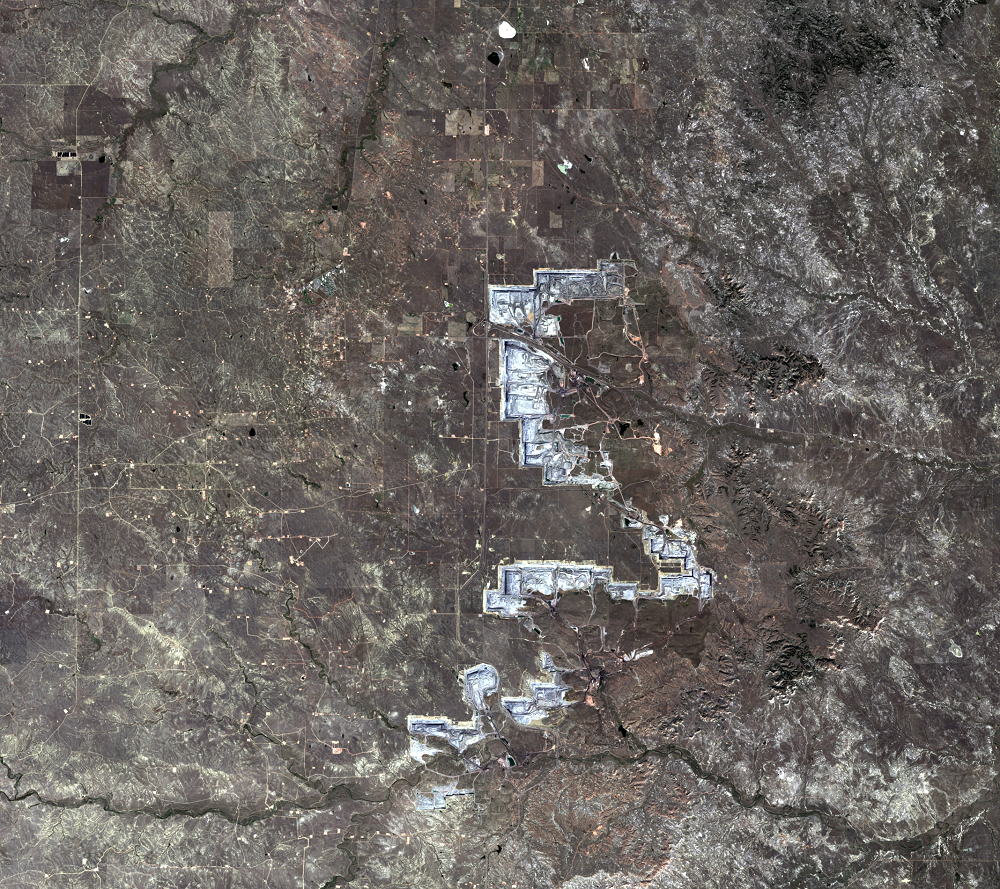
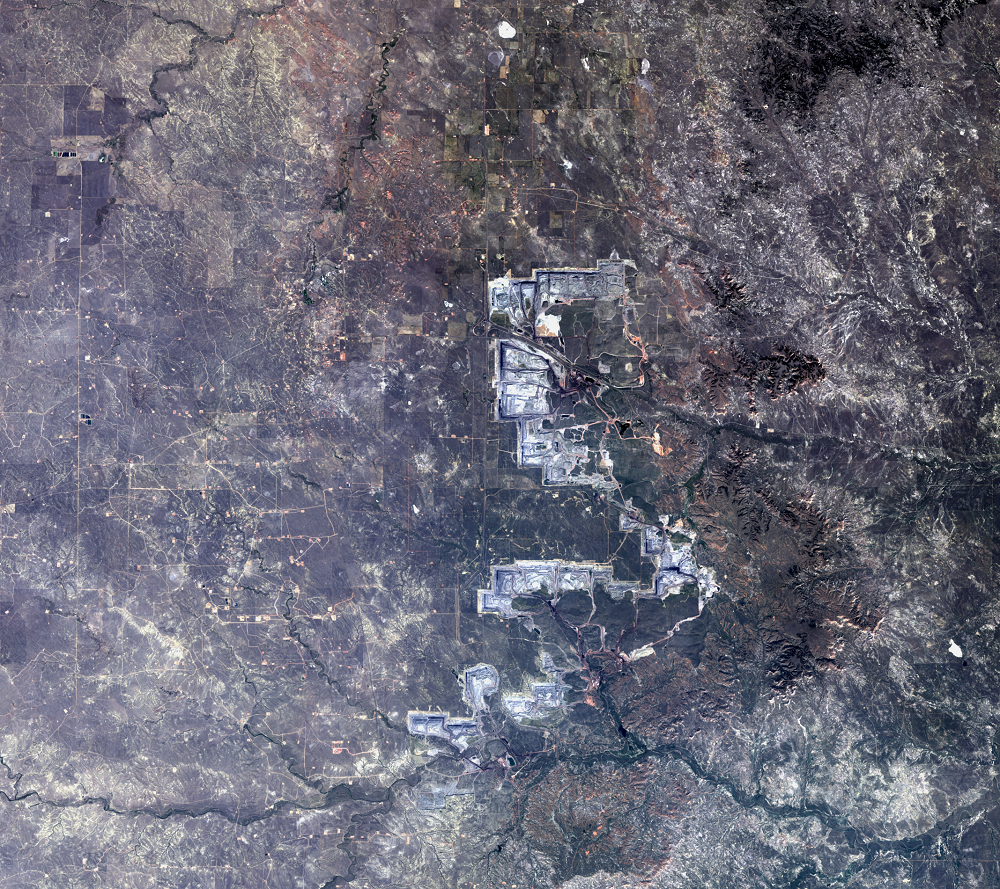
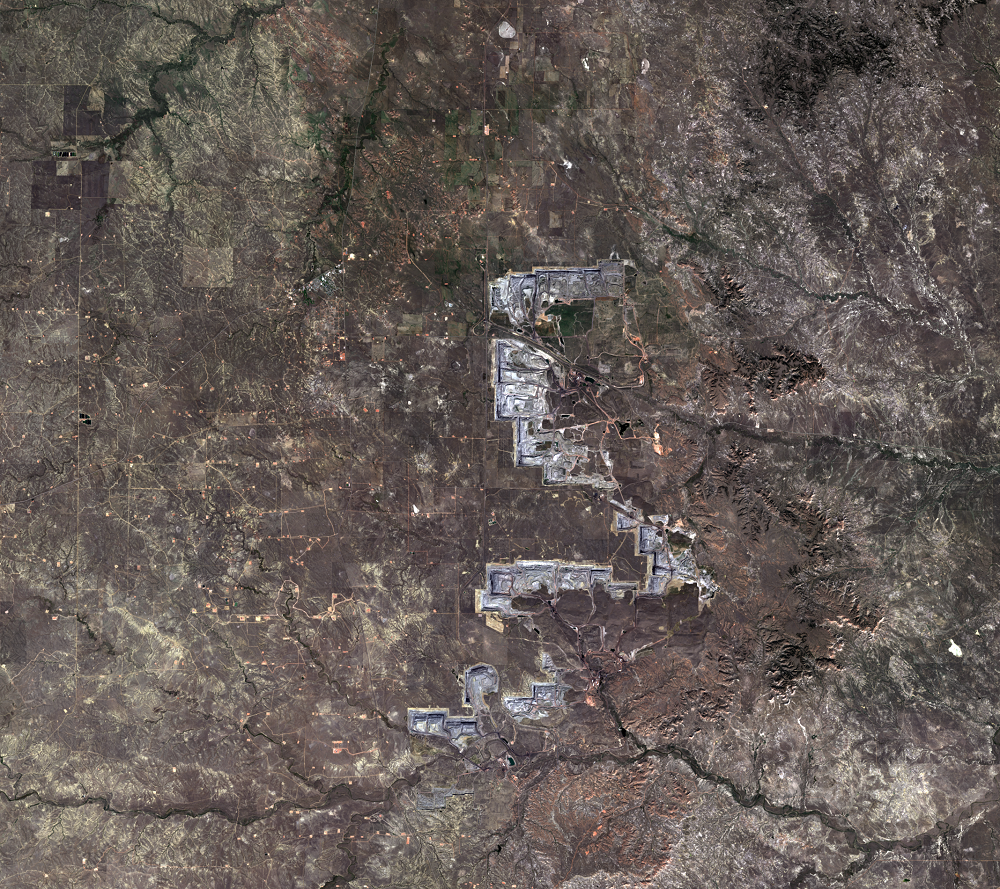
Every day, 100 empty trains enter Wyoming. They leave fully loaded with coal. The United States has the largest coal reserves in the world, and much of it lies in the Powder River Basin (PRB) in Wyoming and Montana. The PRB, which lies between the Black Hills in South Dakota and the Bighorn Mountains in Wyoming, produced 43% of the nation’s coal in 2019.
According to a study by the U.S. Geological Survey, the PRB contains 25 billion tons of economically recoverable coal. This does not mean it’s all mineable. The amount of economically recoverable coal can change based on mining costs and coal prices, which change based on market conditions. Nevertheless, the region has a lot of coal that is very accessible.
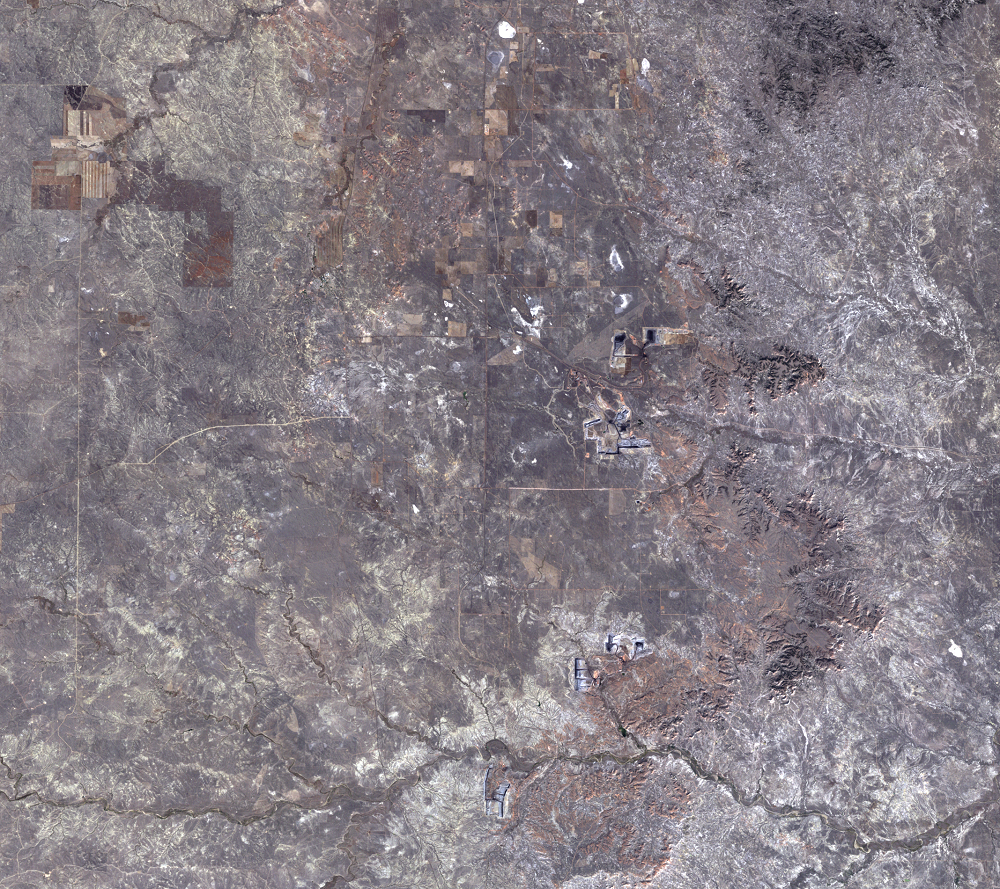
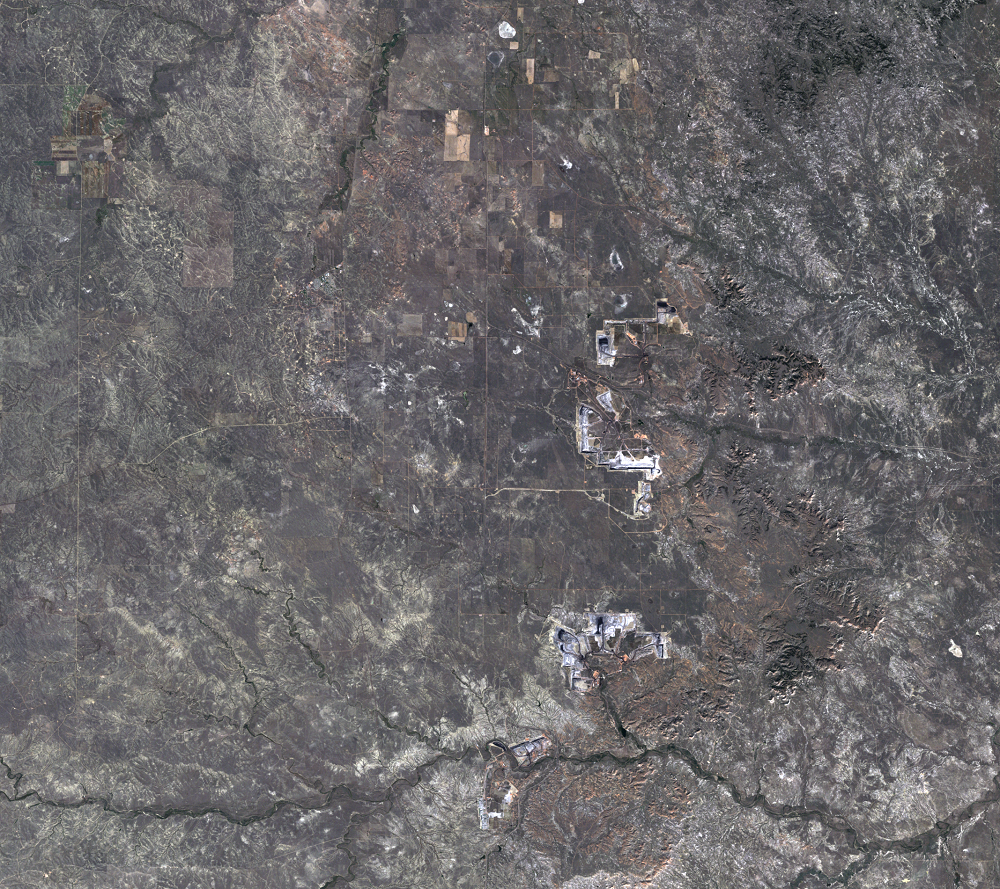
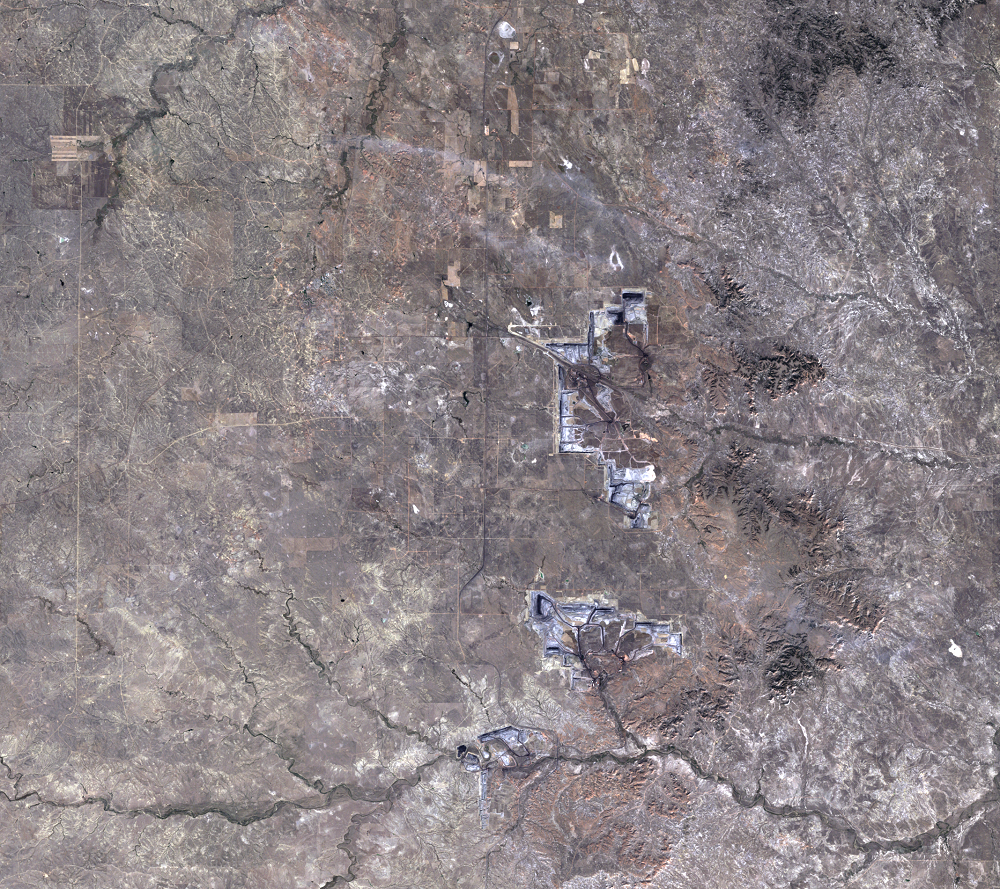
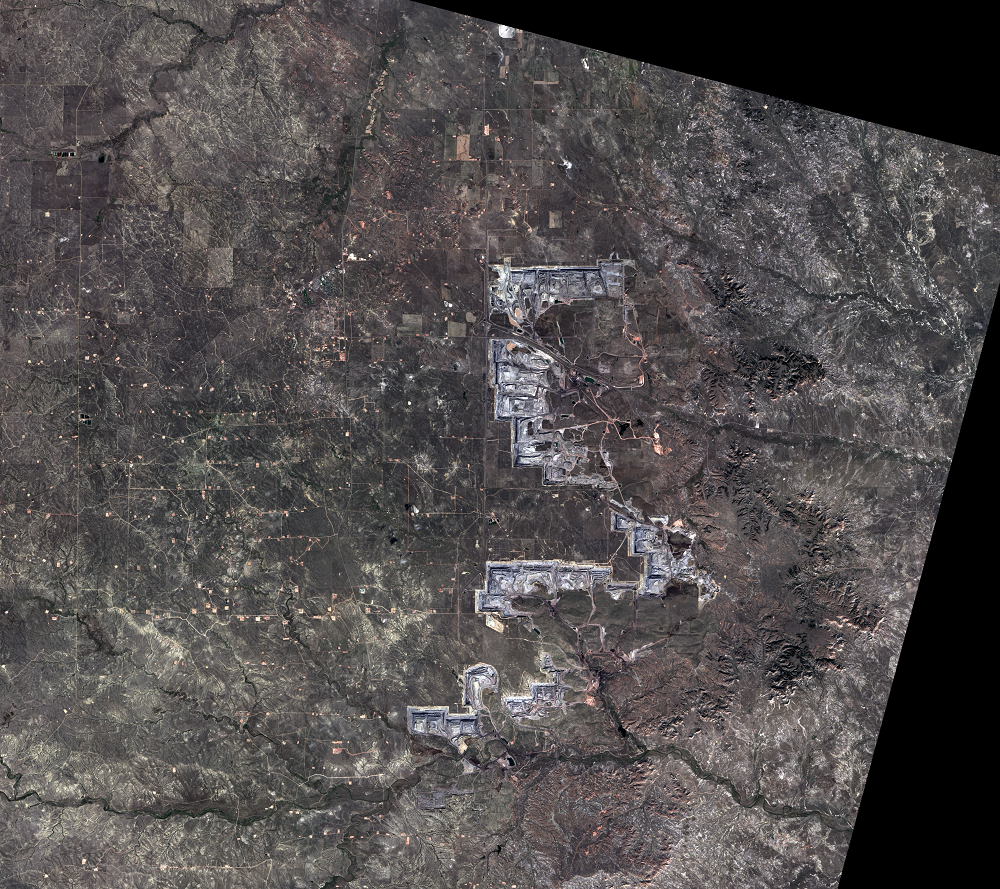
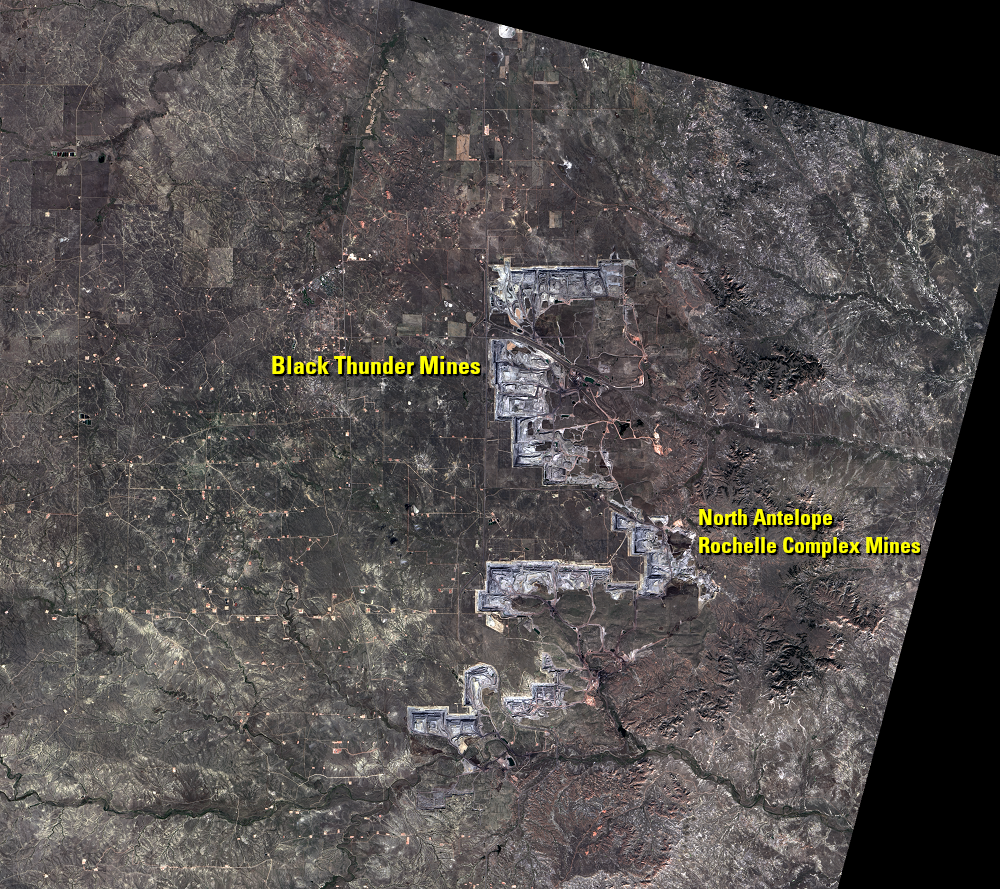
The Black Thunder Mine and the North Antelope Rochelle Complex are two of the largest open-pit mines in the PRB. They lie within the Thunder Basin National Grassland. These mines have been expanding over the past few decades, and the land change is evident in this time series of Landsat images.
Imagery
Every picture has a story to tell
Correlated
Additional story information
Downloads
Anderson, C.L., [n.d.], The Coal Business in Wyoming: Wyoming State Historical Society Web page at http://www.wyohistory.org/encyclopedia/coal-business-wyoming. (Accessed October 17, 2014.)
Arch Coal, [n.d.], Black Thunder Mine—Delivering Energy to America: brochure available at http://www.archcoal.com/aboutus/blackthunder.aspx. (Accessed October 17, 2014.)
BNSF Railway, 2016, Guide to Coal Mines—Mines Served by BNSF Railway: accessed April 27, 2018, at http://www.bnsf.com/ship-with-bnsf/maps-and-shipping-locations/pdf/MineGuide2016.pdf.
Budzik, P., and Perrin, J., 2014, New Petroleum Technology Revitalizes Powder River Basin Oil Production: U.S. Energy Information Administration Web page at http://www.eia.gov/todayinenergy/detail.cfm?id=17971. (Accessed October 17, 2014.)
Bureau of Land Management, 2014, Powder River Basin Coal: BLM Web page at https://eplanning.blm.gov/epl-front-office/eplanning/planAndProjectSite.do?methodName=renderDefaultPlanOrProjectSite&projectId=64842. (Accessed October 17, 2014.)
Demas, A., 2013, Fueling the Mix: Coal and U.S. Electric Power Generation: USGS Science Features Web page available at http://www.usgs.gov/blogs/features/usgs_top_story/fueling-the-mix-coal-and-u-s-electric-power-generation-2/. (Accessed October 17, 2014.)
InfoMine, [n.d.], North Antelope Mine: Mine Sites Web page at http://www.infomine.com/minesite/minesite.asp?site=northantelope. (Accessed October 17, 2014.)
Molnia, C.L., 2013, Map Showing Principal Coal Beds and Bedrock Geology of the Ucross-Arvada Area, Central Powder River Basin, Wyoming: U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Map 3240, 11 p. pamphlet, 1 sheet, scale 1:50,000. (Available online at http://pubs.er.usgs.gov/publication/sim3240.)
NASA, 2005, North Antelope Rochelle Coal Mine, Wyoming: NASA Earth Observatory, available at http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=5915. (Accessed October 17, 2014.)
Natural Gas Intelligence (NGI), 2014, Information on the Powder River Basin: NGI’s Shale Daily, Web page at http://www.naturalgasintel.com/powderriverinfo. (Accessed November 25, 2014.)
Ostlind, E., [n.d.], The Powder River Basin: A Natural History: Wyoming State Historical Society Web page at http://www.wyohistory.org/encyclopedia/powder-river-basin-natural-history. (Accessed October 17, 2014.)
Peabody Energy, 2014, North Antelope Rochelle Mine: Peabody Energy Web page at https://www.peabodyenergy.com/Operations/U-S-Mining/Powder-River-Basin-Mining/North-Antelope-Rochelle-Mine. (Accessed October 17, 2014.)
Scott, D.C., and Luppens, J.A., 2013, Assessment of Coal Geology, Resources, and Reserve Base in the Powder River Basin, Wyoming and Montana: U.S. Geological Survey Fact Sheet 2012–3143, 6 p. (Available online at http://pubs.er.usgs.gov/publication/fs20123143.)
U.S. Code, [n.d.], U.S. Code Chapter 25—Surface Mining Control and Reclamation, in Title 30—Mineral Lands and Mining, § 1265—Environmental Protection Performance Standards: available at the Legal Information Institute at http://www.law.cornell.edu/uscode/text/30/1265. (Accessed October 17, 2014.)
Western Organization of Resource Councils, 2011, Exporting Powder River Basin Coal: Risks and Costs: WORC report available at http://www.worc.org/publication/exporting-powder-river-basin-coal-risks-and-costs. (Accessed October 17, 2014.)
Wyoming Mining Association, 2014, Coal: Wyoming Mining Association Web page at http://www.wyomingmining.org/minerals/coal/. (Accessed October 17, 2014.)
Wyoming Mining Association, 2014, The 2013–14 Concise Guide to Wyoming Coal: Wyoming Mining Association report available at http://www.wyomingmining.org/minerals/coal/. (Accessed October 17, 2014.)