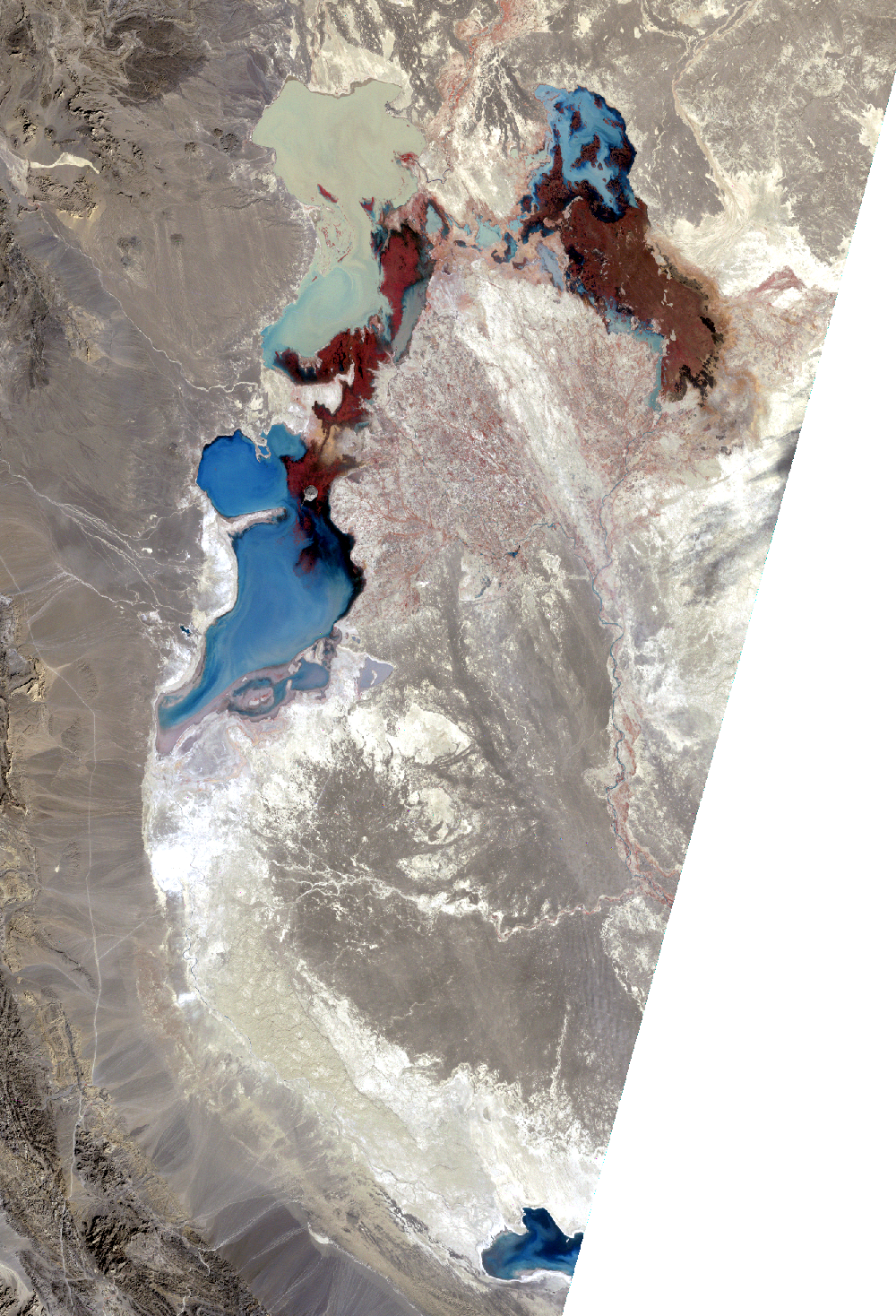
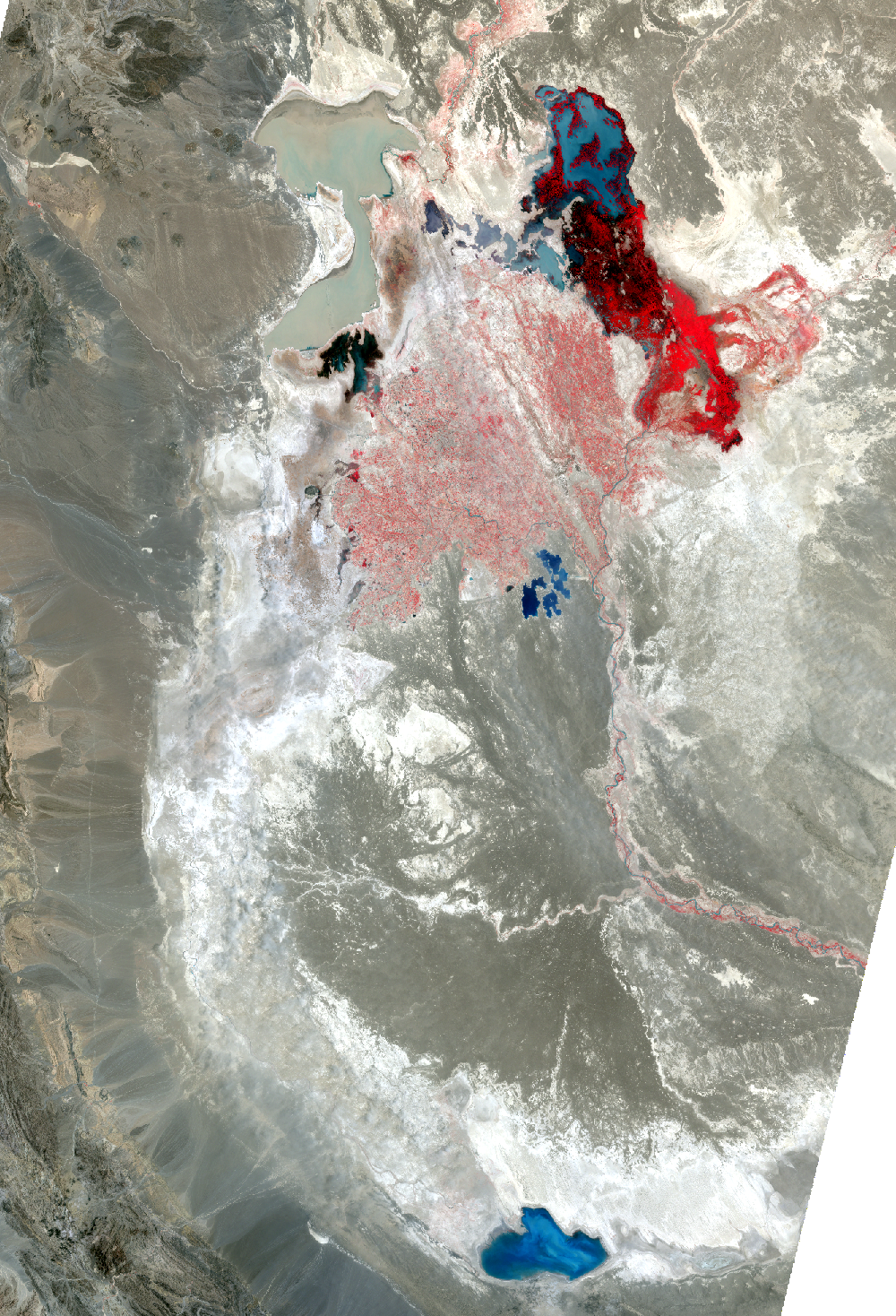
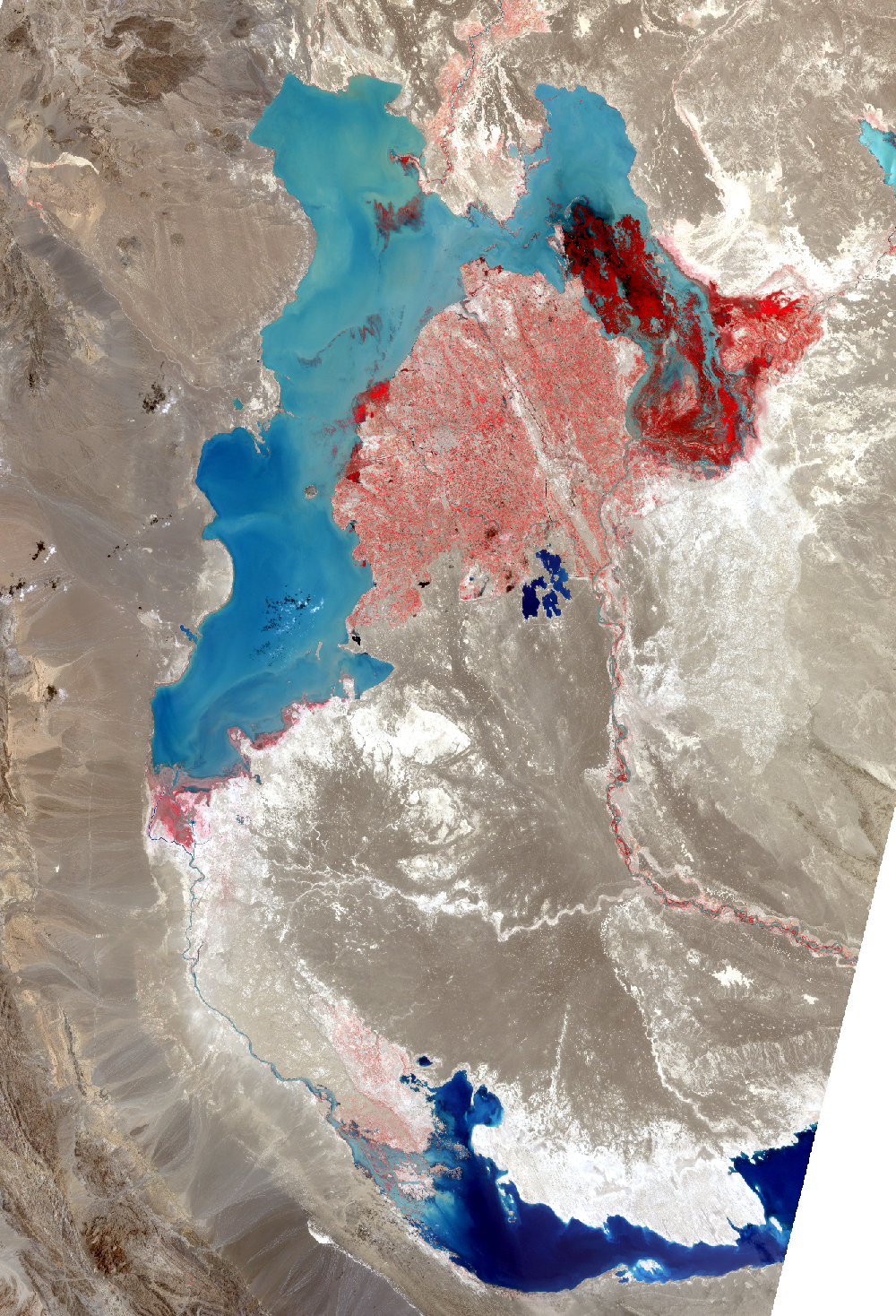
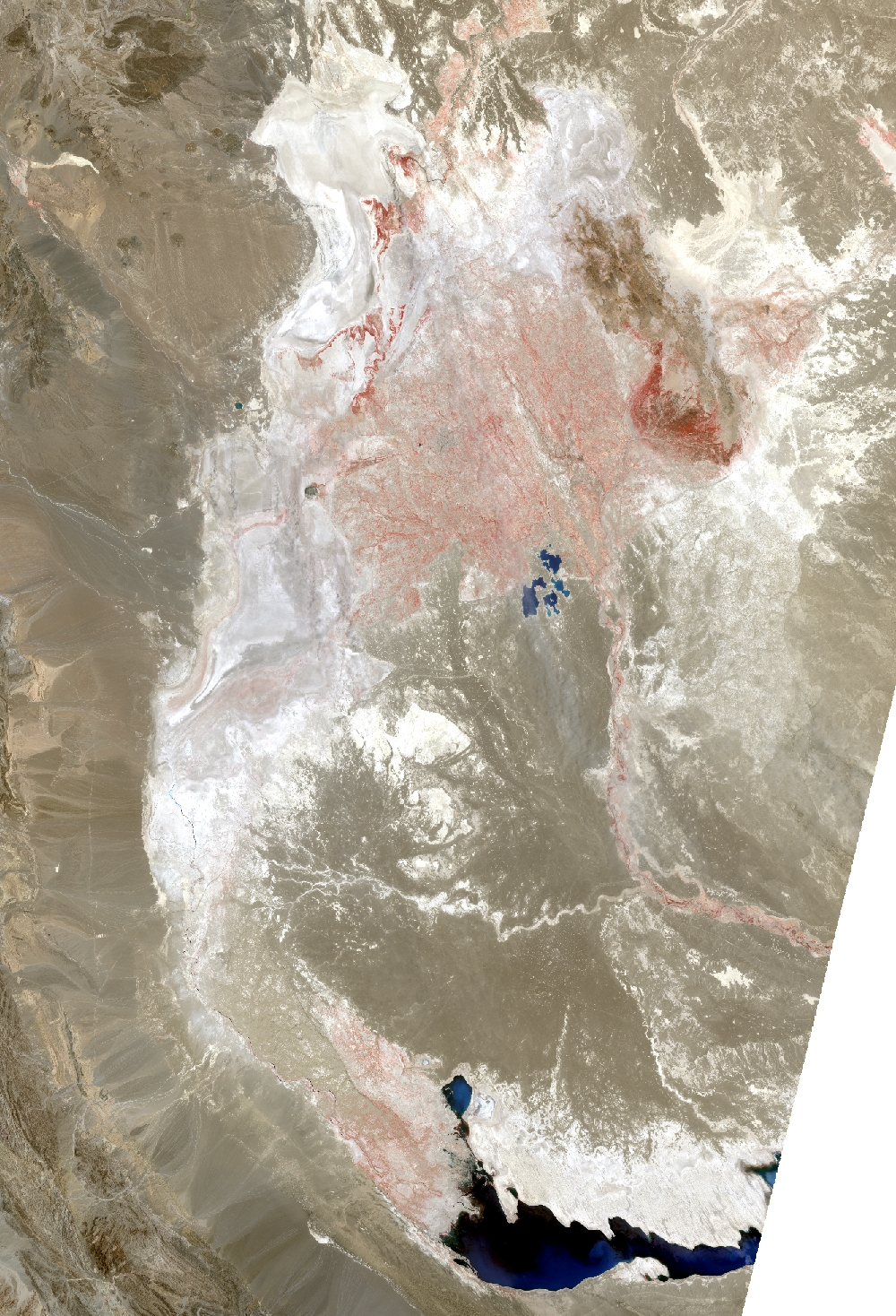
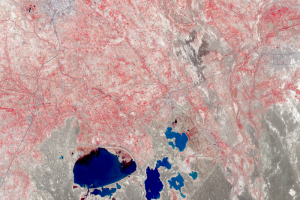
Lake Hamoun, Iran and Afghanistan
Earth Resources Observation and Science (EROS) Center - Earthshots
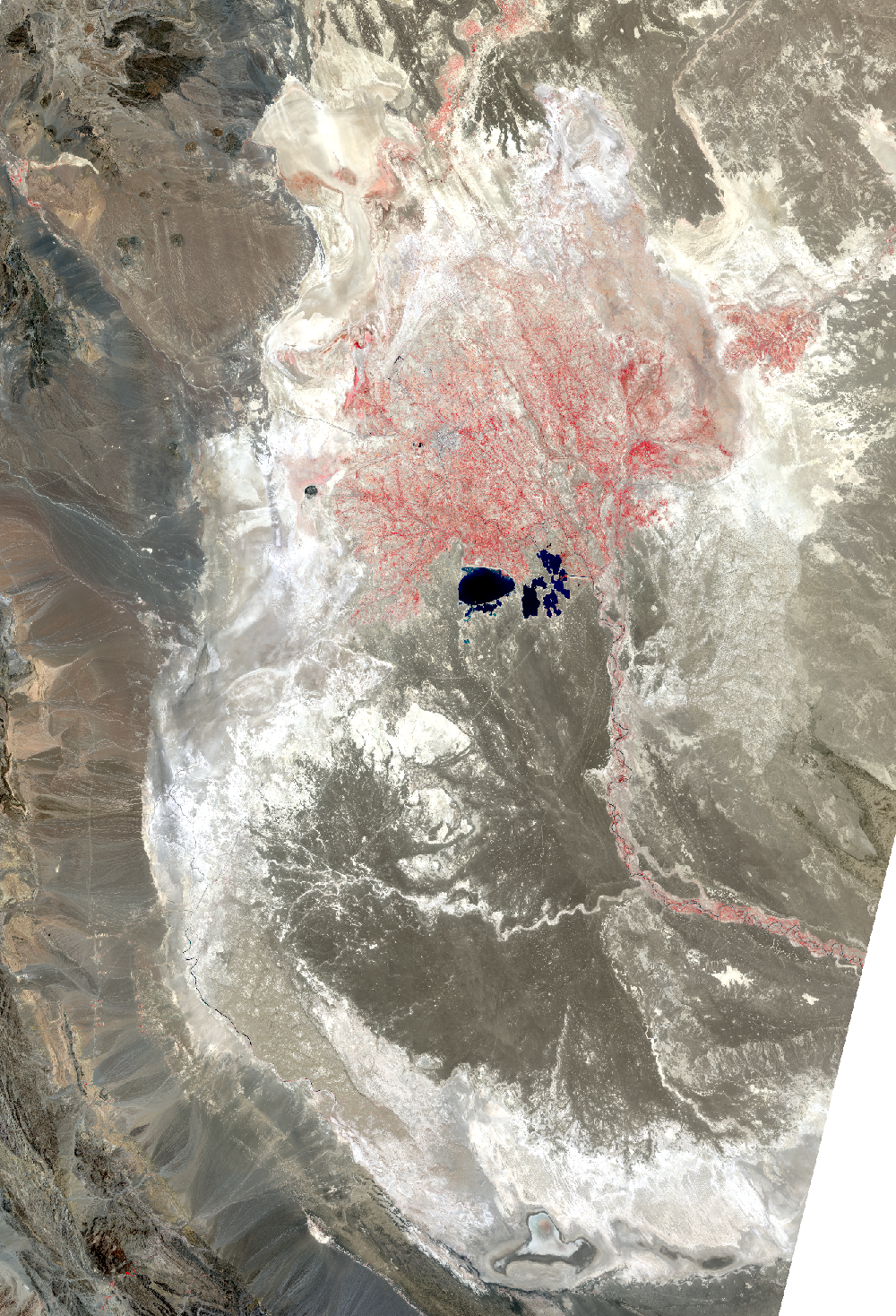
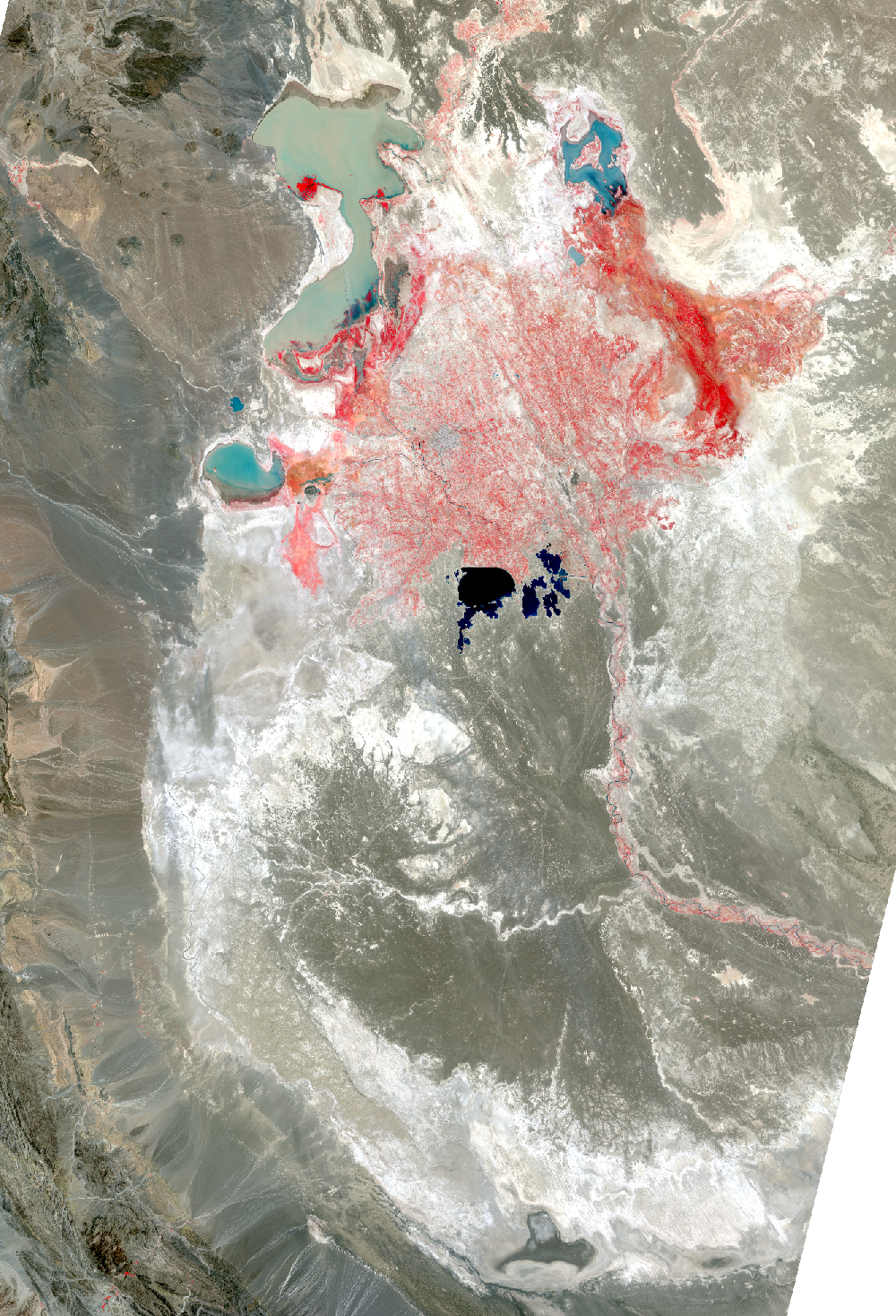
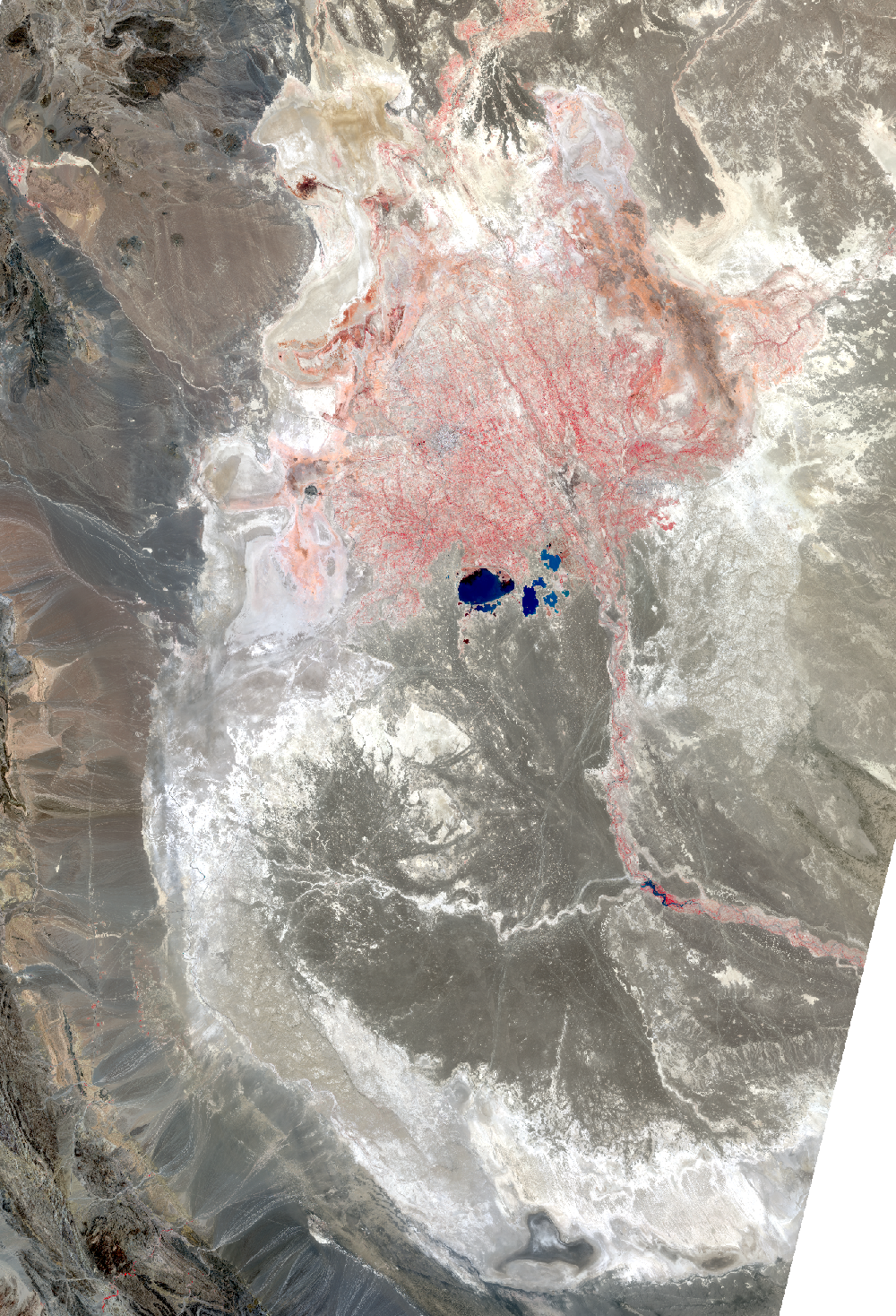
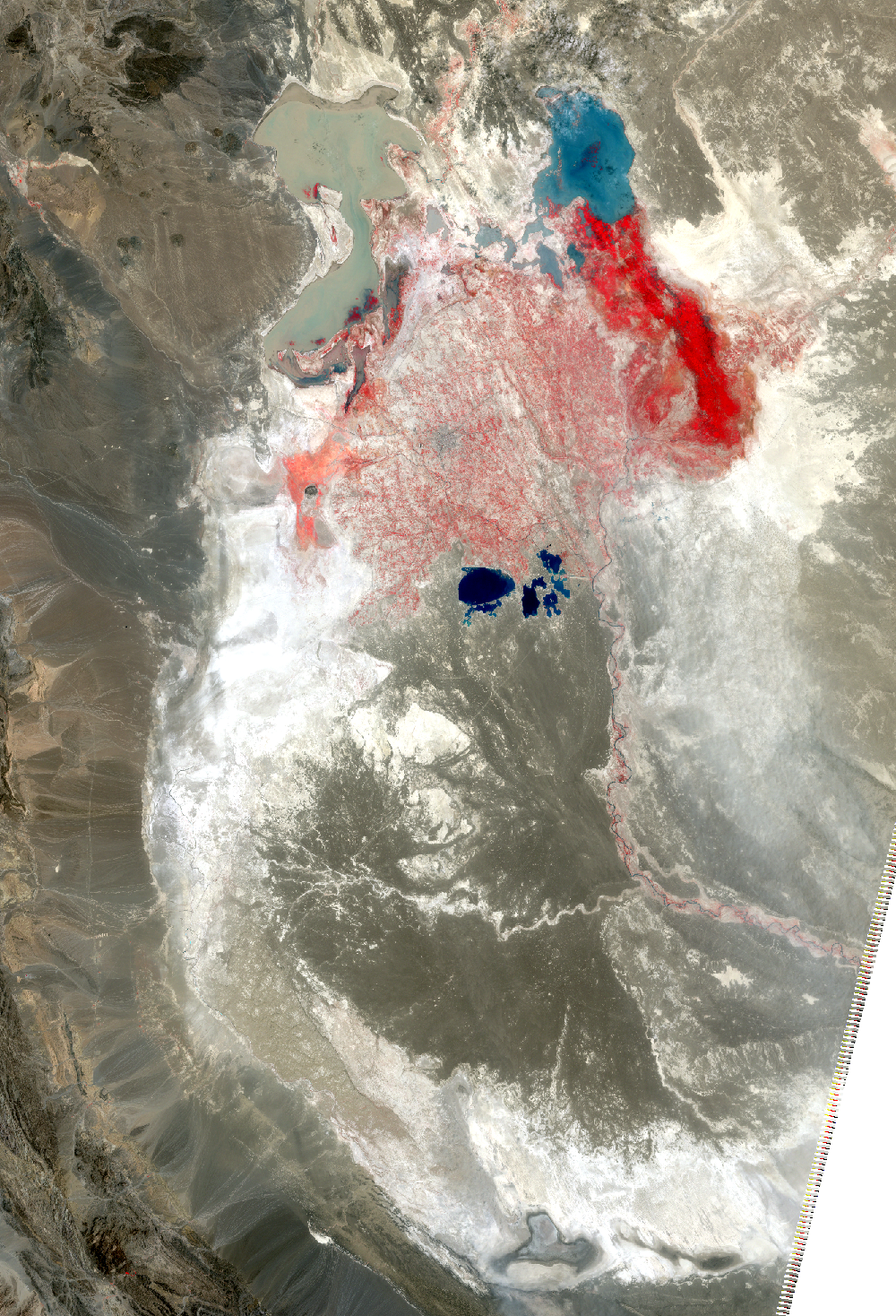
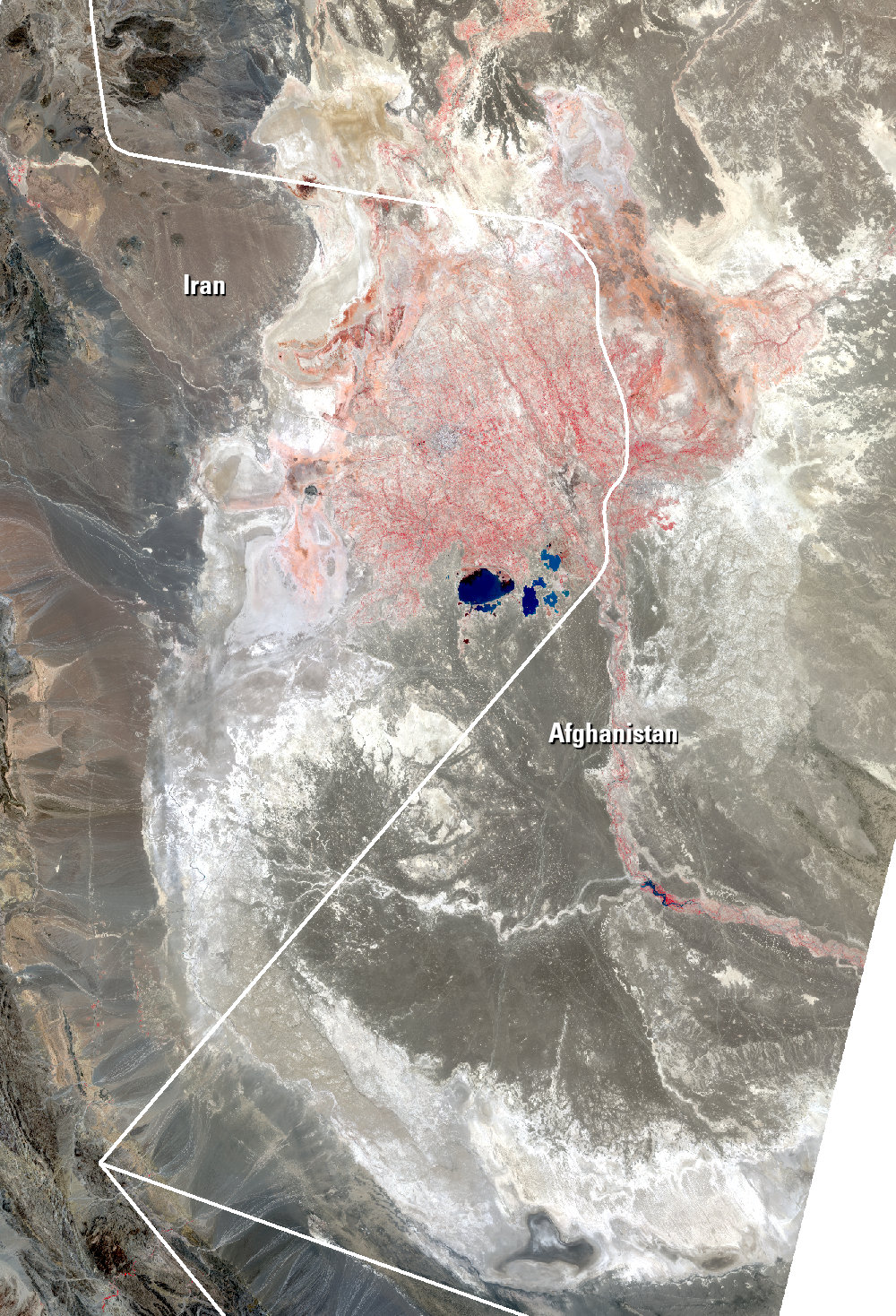
The Sistan Basin lies on the Iran-Afghanistan border. Melted snow from the Hindu Kush Mountains of Afghanistan nourishes this dry basin. The Helmand River carries the snowmelt across the Margo Desert and into the Sistan Basin, where the water pools into Lake Hamoun. Sometimes anyway. Lake Hamoun is seasonal, and water is generally only present during the spring melt season.
Surrounded by hundreds of kilometers of arid plains, the Sistan Basin is in one of the driest regions of the world, so the three shallow lakes that make up Hamoun naturally expand and contract in the wet to dry seasons. These lakes and wetlands once supported great plant and animal diversity. But the combination of drought and water diversion for irrigation has caused Lake Hamoun to nearly disappear, along with the local bird and fish populations.
Imagery
Downloads
Esmaili, O., Tajrishy, M., and Arasteh, P.D., 2006, Evaluation of dust sources in Iran through remote sensing and synoptical analysis, in Atlantic Europe Conference on Remote Imaging and Spectroscopy, University of Central Lancashire, Preston, UK, 11–12 September 2006, AECRIS 2006 Proceedings: p. 136–143.
Partow, H., ed., 2006, History of Environmental Change in the Sistan Basin Based on Satellite Image Analysis—1976–2005: Nairobi, Kenya, United Nations Environment Programme, 56 p.
Rajaei, G., Mansouri, B., Jahantigh, H., and Hamidian, A.H., 2012, Metal Concentrations in the Water of Chah Nimeh Reservoirs in Zabol, Iran: Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, v. 89, no. 3, p. 495–500. (Also available online at http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs00128-012-0738-0.)
Sharifikia, S., 2013, Environmental challenges and drought hazard assessment of Hamoun Desert Lake in Sistan region, Iran, based on the time series of satellite imagery: Natural Hazards, v. 65, p. 201–217. (Also available online at http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11069-012-0353-8.)
United Nations Development Programme, 2008, Restoration, Protection and Sustainable Use of the Sistan Basin: International Waters Learning Exchange & Resource Network Web page at http://iwlearn.net/iw-projects/2130. (Accessed December 2, 2013.)
Weier, J., 2002, From Wetland to Wasteland—The Destruction of the Hamoun Oasis: NASA Earth Observatory, available online at http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/hamoun/. (Accessed December 2, 2013.)
World Cities, 2013, Zabol: World Cities, Encyclopedia of World Populations, available online at http://www.worldcities.us/Zabol/. (Accessed December 2, 2013.)