The USGS Upper Midwest Environmental Sciences Center is working with the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers to identify forest canopy gaps in riparian forests along the Mississippi and Illinois Rivers. The goal is to help understand the factors affecting floodplain forest regeneration and how these factors might be managed. To locate the canopy gaps, lidar data were collected for the areas of interest and a canopy height model was created. Areas of at least 18 meters in diameter with canopy heights of less than 10 meters were classified as canopy gaps. Lidar-detected forest canopy gaps were then randomly selected for field testing and data collection to determine forest health metrics in and surrounding the canopy gap.
The data collected from these sample plots will assist resource managers in identifying which factors inhibit or promote floodplain forest regrowth. With the acquisition of new lidar data, change analyses will be possible to further inform riparian forest management within the Mississippi and Illinois River floodplains.
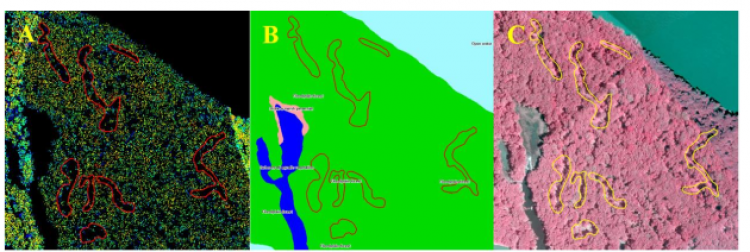
A portion of Railroad Island in the Upper Mississippi River Wildlife and Fish Refuge located about 20 miles SW of Dubuque Iowa. Tile A showing the lidar point cloud along the eastern short of Railroad Island in Pool 13 with gaps delineated, Tile B showing how these gaps align with the existing 2010 systemic vegetation layer, and Tile C showing these same gaps in the 2010 systemic CIR imagery set. The images are oriented with north at the top and show an area 700-meters E-W by 700-meters N-S.