This project utilizes Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) to identify and monitor small-scale mining dredges operating on rivers in Guyana, South America. River dredging is an elusive activity that can be difficult to monitor using optical imagery due to the small spatial footprint, remote operating areas, and excessive cloud cover common to South America. SAR is an active remote sensing technology that uses longer wavelength signals (2–100 centimeters) that are unobstructed by weather and can be collected day or night. SAR signals that interact with manmade objects, such as river mining dredges, create strong backscatter signals compared to their surrounding environment. These high-intensity signals can be statistically identified and then extracted using semi-automatic techniques that are adapted from ocean ship detection methods. Identifying dredges using SAR techniques provides a picture of riverine mining activity that may help monitor compliance with regulations and assess environmental impacts.
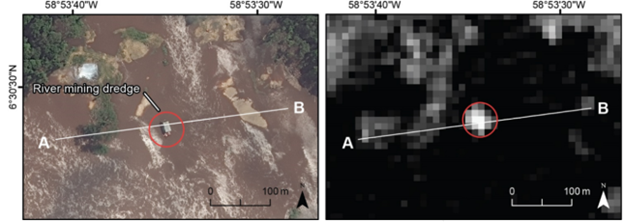
(Left) World-View-1 optical satellite imagery of a mining dredge operating on the Cuyuni River in Guyana on July 6, 2022; (right) RADARSAT-2 SAR data of the same date and location. Points A and B in the pictures are used for location context when developing profile plots of SAR backscatter strength.
Disclaimer: Any use of trade, firm, or product names is for descriptive purposes only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Government.