The Landsat Program is a joint effort of the USGS and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) to gather Earth resource data using a series of land-observing satellites. Whereas NASA’s role is the development and launch of Earth-observing instruments and spacecraft, the USGS is responsible for flight operations, maintenance, and management of all ground data reception, processing, archiving, product generation, and distribution. For 41 years, a primary objective of the Landsat Program has been to record land-surface conditions across the global land surface through the collection of consistently calibrated image data.
In spring 2013, the USGS decommissioned Landsat 5 following an extraordinary 28 years of imaging operations, which earned it an official Guinness World Record. Shortly thereafter, the USGS assumed ownership and operation of Landsat 8 following NASA’s launch and on-orbit checkout. Data from the new satellite proved to be in great demand, thanks in part to NASA’s imaging-sensor improvements that included greatly improved signal-to-noise ratio, 12-bit quantization, a new coastal blue band (for detection of water column constituents), a new cirrus band (for better cloud screening), and an additional thermal band (for more precise temperature measurements).
The Landsat team at the USGS EROS Center ingested over 516,000 new images from Landsats 5, 7, and 8 into the Landsat archive during FY13, plus nearly 1.4 million historical Landsat images provided by current or former International Cooperator receiving stations. During the same period, users downloaded nearly 4.4 million Landsat scenes from EROS servers.
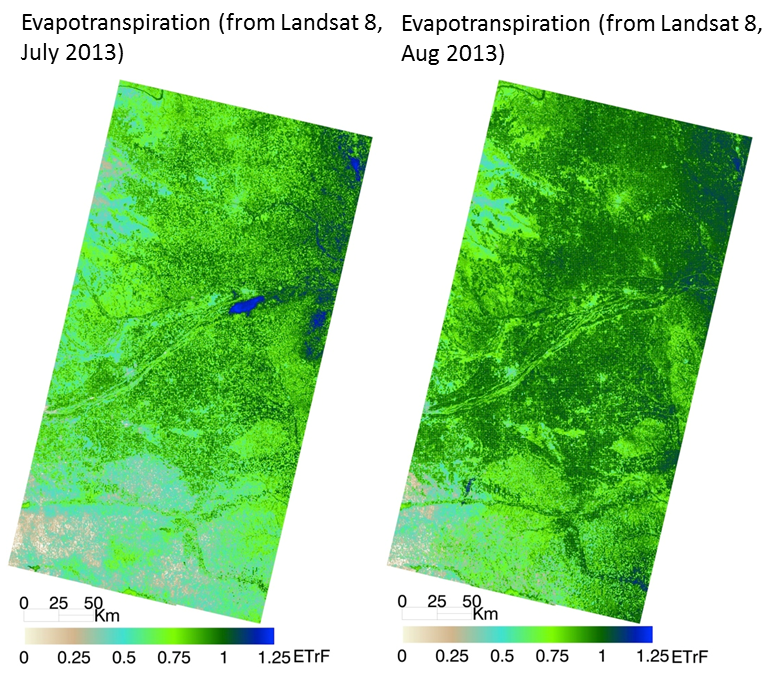
Nebraska’s Central Platte Natural Resources District uses Landsat-based estimates of water use to manage the Ogallala Aquifer. (METRIC model pioneered by the Idaho Department of Water Resources, University of Idaho, and the Landsat Science Team.)