Large-scale plant productivity in coastal marshes needs to be quantified to understand marsh resilience to sea-level rise, to help define eligibility for carbon offset credits, and to monitor impacts from land use, eutrophication, and contamination. Remote monitoring of aboveground biomass of emergent wetland vegetation will help address this need. Differences in sensor spatial resolution, bandwidth, temporal frequency, and cost constrain the accuracy of biomass maps produced for management applications. In addition, the use of vegetation indices to map biomass may not be effective in wetlands due to confounding effects of water inundation on spectral reflectance. To address these challenges, we used partial least squares regression to select optimal spectral features in situ and with satellite reflectance data to develop predictive models of aboveground biomass for common emergent freshwater marsh species, Typha spp. and Schoenoplectus acutus, at two restored marshes in the Sacramento-San Joaquin River Delta, California. We used field spectrometer data to test model errors associated with hyperspectral narrowbands and multispectral broadbands, the influence of water inundation on prediction accuracy, and the ability to develop species-specific models. We used Hyperion data, DigitalGlobe WorldView-2 (WV-2) data, and Landsat 7 data to scale up the best statistical models of biomass. Field spectrometer-based models of the full dataset showed that narrowband reflectance data predicted biomass somewhat, though not significantly better than broadband reflectance data. However, hyperspectral first derivative reflectance spectra best predicted biomass for plots where water levels were less than 15 cm. The Landsat 7 dataset (7 images) predicted biomass slightly better than the WV-2 dataset (6 images). The Hyperion dataset (1 image) was least successful in predicting biomass. Shortwave infrared bands on 30-m resolution Hyperion and Landsat 7 sensors aided biomass estimation; however, managers need to weigh tradeoffs between cost, additional spectral information, and high spatial resolution that will identify variability in small, fragmented marshes common to the Sacramento-San Joaquin River Delta and elsewhere in the Western United States.
Byrd et. al. 2014. Remote Sensing of Environment. In Press.
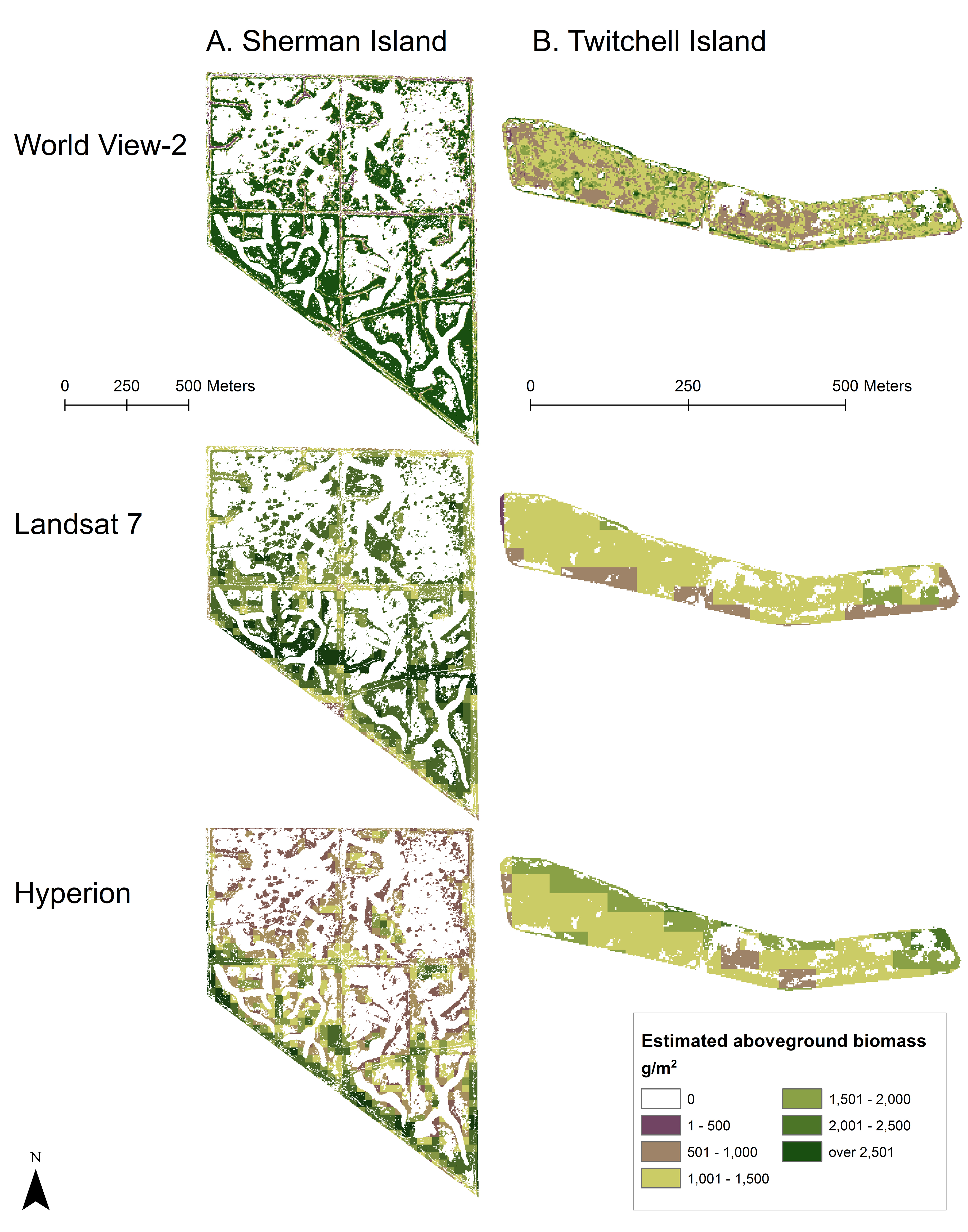
Maps of estimated biomass for late-summer Hyperion, Landsat 7, and WorldView-2 images for a) Sherman Island and b) Twitchell Island. Biomass was mapped for pixels classified as emergent marsh vegetation (Typha spp. and/or S. acutus) or plant litter.