The USGS Earth Resources Observation and Science (EROS) Science Processing Architecture (ESPA) has been developed as the computing infrastructure to generate climate data record (CDR) and essential climate variable (ECV) products. The current ESPA configuration includes 184 processing cores and 30 terabytes of online storage. The Landsat Ecosystem Disturbance Adaptive Processing System (LEDAPS) has been integrated into ESPA to generate the surface reflectance CDR products needed to develop the surface water, burned area, and snow cover ECVs. The ECV project has an introductory Web page on the Land Remote Sensing Program Web site (http://remotesensing.usgs.gov/ecv.php) and is developing a comprehensive project Web site describing CDR and ECV product development activities.
Initial versions of the algorithms for the surface water, burned, and snow-covered area ECVs have been integrated into the ESPA. Nationwide test sites have been defined for model calibration and to validate the surface water extent and burned area ECV products. A topographic slope module that was developed for the snow-covered area product is being used to augment the spectral indices to detect surface water. The MTBS is being used to develop training statistics and validation data for the burned area products. A boosted regression tree model has been developed to classify burned areas with a quality assessment/confidence estimate. Model parameters are being refined using training data sampled by ecoregion. Single date and annual summary product specifications have been defined.
In collaboration with the University of California Santa Barbara and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, fractional snow covered area products are being developed from MODIS and Landsat (TM and ETM+) data to downscale the MODIS 500-m snow cover products to 30-m resolution. A statistical sampling design has been developed to validate the global 30-m land cover continuous field products. High-resolution commercial satellite data have been acquired for North and South America for validation studies. A global percent tree cover dataset for 2010 has been created and will be the focus of validation efforts over the next several months.
Field data collection protocols and procedures have been developed to validate leaf area index (LAI) products created from airborne and satellite data. The Committee on Earth Observation Satellites (CEOS) Land Product Validation site data are being investigated for ECV product validation. The product maturity matrix developed by NOAA being reviewed by the CEOS Working Group on Climate has been adapted to define a numerical rating for product validation. The Digital Image and Remote Sensing Image Generation (DIRSIG) software developed at the Rochester Institute of Technology is being used to generate simulated datasets by controlling the physical parameters (e.g. vegetation structure, optical properties). These data can be used to calibrate and validate algorithm and model parameters, because existing measurement datasets are often insufficient (geographic coverage, uncertainties) and expensive to collect. The DIRSIG modeling software has broad applicability for validation of more than just the biomass ECV algorithm. Empirical relationships between multispectral surface reflectance and lidar point cloud data are being developed to generate predictive models of height above ground estimates of forest canopy. The initial model was developed using WELD and it has been refined using surface reflectance retrievals from the GLS2005 data. Preliminary data products have been developed for the conterminous United States and for a region of Nepal.
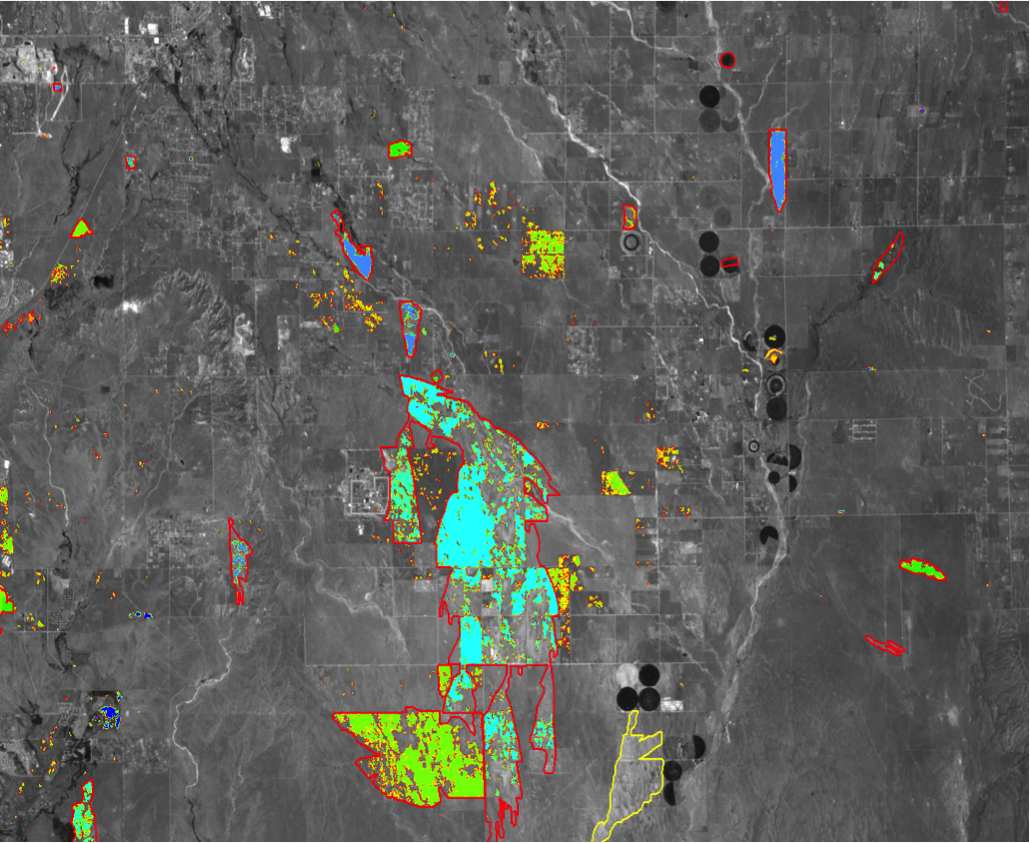
Example of the annual summary burned area essential climate variable (ECV) product for an area in Colorado for 2008. The colors in the legend identify the month in which the burned area was first identified. The fire perimeters are outlined in red.
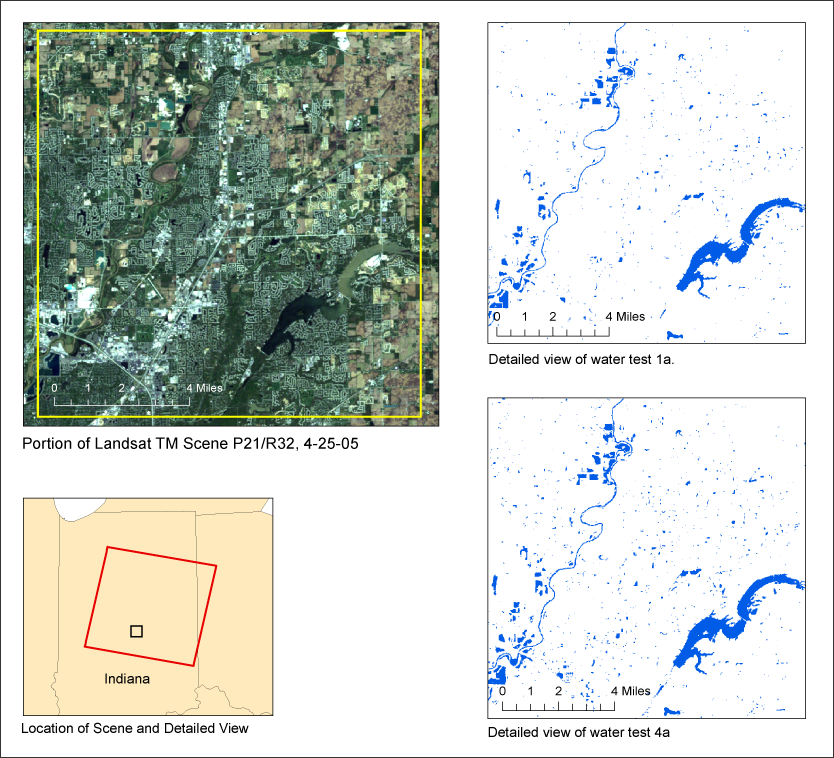
The USGS is developing methods to map surface water extent from any Landsat TM or ETM+ scene in the archive. Here, results from two different methods are provided for one of the 35 test areas selected across the North American continent, Hawaii and Puerto Rico.